By Suzanne Leigh
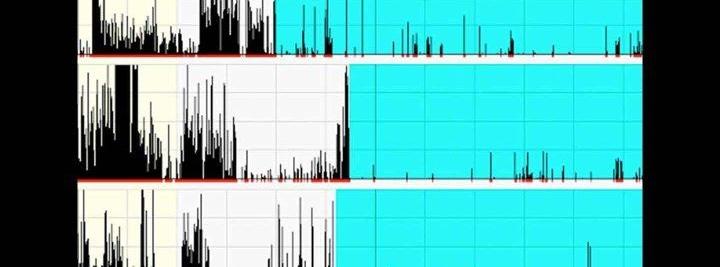
Wrist devices captured five participants' movements throughout the day. The yellow section represents day, white evening and blue sleep. The top data set shows the most disrupted sleep. Image by Yue Leng, Kristine Yaffe, Kristen Knutson
A study in Neurology, led by Yue Leng, PhD, and Sasha Milton, followed the sleep patterns of 733 older female participants to see if specific patterns of change were associated with a higher risk of dementia. The participants, whose average age was 83, were monitored by wrist devices that track movement and time spent asleep. They had normal cognition at the start of the study.
What they discovered
At the end of the study, five years later, 13% had developed dementia. This included 25 participants (8%) with stable sleep patterns, 39 (15%) with declining nighttime sleep patterns and 29 (19%) with increasing sleepiness. After adjusting for factors like age, education, diabetes and hypertension, those with increasing sleepiness had double the risk of the stable sleepers.
Why it matters
This study is one of the first to look at how sleep patterns change over time and relate to dementia risk. It adds to a body of recent UCSF-led research that shows poor sleep quality in midlife, delayed dream phase and extended napping are linked to a higher risk of dementia.
Need to know
It is unknown if worsening sleep increases the risk of dementia or if dementia leads to worsening sleep. Some scientists believe both theories may be correct.
Funding: National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Aging
Read the study
About UCSF Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences
The UCSF Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and the Langley Porter Psychiatric Institute are among the nation's foremost resources in the fields of child, adolescent, adult, and geriatric mental health. Together they constitute one of the largest departments in the UCSF School of Medicine and the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, with a focus on providing unparalleled patient care, conducting impactful research, training the next generation of behavioral health leaders, and advancing diversity, health equity, and community across the field.
UCSF Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences conducts its clinical, educational, and research efforts at a variety of locations in Northern California, including the UCSF Nancy Friend Pritzker Psychiatry Building; UCSF Langley Porter Psychiatric Hospital; UCSF Health medical centers and community hospitals across San Francisco; UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospitals in San Francisco and Oakland; Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital and Trauma Center; the San Francisco VA Health Care System; UCSF Fresno; and numerous community-based sites around the San Francisco Bay Area.
About the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences
The UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences, established by the extraordinary generosity of Joan and Sanford I. "Sandy" Weill, brings together world-class researchers with top-ranked physicians to solve some of the most complex challenges in the human brain.
The UCSF Weill Institute leverages UCSF’s unrivaled bench-to-bedside excellence in the neurosciences. It unites three UCSF departments—Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Neurology, and Neurological Surgery—that are highly esteemed for both patient care and research, as well as the Neuroscience Graduate Program, a cross-disciplinary alliance of nearly 100 UCSF faculty members from 15 basic-science departments, as well as the UCSF Institute for Neurodegenerative Diseases, a multidisciplinary research center focused on finding effective treatments for Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and other neurodegenerative disorders.
About UCSF
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is exclusively focused on the health sciences and is dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. UCSF Health, which serves as UCSF’s primary academic medical center, includes top-ranked specialty hospitals and other clinical programs, and has affiliations throughout the Bay Area.





